Both techniques are used to create models that give us better results from simpler models.
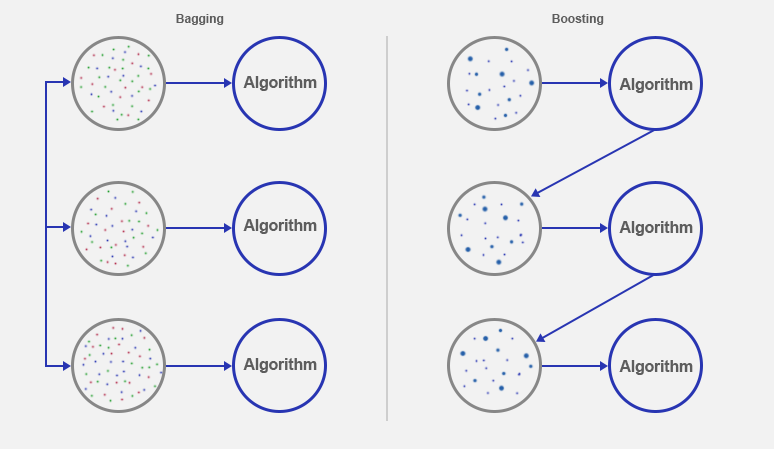
On the one hand, bagging is responsible for running in parallel N times a simple algorithm and the most repeated (or average) is chosen by a voting system.
On the other hand, boosting is executed sequentially because each output of each algorithm is used to learn and assign weights depending on the previous errors.
Therefore, the main difference is that the bagging uses the algorithms independently and the boosting weights according to the previous errors.
If you want more information, an example of boosting is the adaboost and an example of bagging is the random forest.